As a kid growing up, I remember my mother and grandmother giving me a vitamin C capsule every day. Now that I am a grandmother I wondered about the effects of type 1 and vitamin C.
I mean if I were to give my type 1 diabetic grandson vitamin C, what effect would that have on his blood sugars, or would it affect it at all?
Would it maybe help stabilize his blood sugars more?
Maybe help any small wounds heal faster?
Perhaps it could even prevent nerve damage leading to so many complications?
I believe that in order to discover the effects of type 1 and vitamin C we first need to understand just exactly what is vitamin C?
Table of Contents
What is vitamin C?
Simply put, vitamin C is a vital nutrient that helps form and maintain bones, skin, blood vessels and can serve as an antioxidant.
Vitamin C can is also referred to as L-ascorbic acid, ascorbic acid, or L-ascorbate.
Why do we need vitamin C
Did you know that vitamin C is water-soluble and that as humans, our bodies can’t store it?
This is why we need to eat it from our food or supplements daily.
Vitamin C helps our bodies with a variety of essential functions including:
- helps produce collagen, L-carnitine, and some neurotransmitters
- acts as an antioxidant, removing unwanted substances known as reactive oxidative species (ROS) from the body
- helps us absorb iron
- boosts our immune system
- enhances wound healing
- prevent scurvy
Based on that list Vitamin C is pretty important to us.
What foods contain vitamin C?

Getting enough vitamin C from our food isn’t as difficult as you might think. There are plenty of fruits and vegetables containing high amounts of vitamin C including:
- Guavas – contain 419% DV(daily value) (377mg)per cup 112 calories
- Kiwifruit – contain 185% DV (167mg)per cup 110 calories
- Bell peppers – contain 169% DV (daily value)(152mg) per cup 31 calories
- Strawberries – 108% DV (98mg) per cup 53 calories
- Oranges – 106% DV (96)per cup 85 calories
- Papaya – 98% DV (daily value)(88mg) per cup 62 calories
- Broccoli – 90% DV (81mg)per cup 31 calories
- Tomato – 61% DV (55mg)per cup 43 calories
- Snow peas – 42% DV (daily value) (38mg)per cup 26 calories
- Kale – 26% DV (23mg)per cup 47 calories
How Much do we need?
The recommended daily allowance of vitamin C for adults over 19 years of age are:
- men – 90 mg daily
- women – 75 mg daily
- during pregnancy and lactation that increases to 85 – 120 mg daily
- smoking can deplete vitamin C so smokers should consume an additional 35 mg daily beyond the recommended daily dosage.
Since vitamin C is water-soluble and doesn’t accumulate in the body overdose is highly unlikely. Keep in mind the source of vitamin C is fruits and vegetables, which can cause diarrhea or stomach cramps if you have overindulged.
Another thing to consider when using food as your source of vitamin C if you are a diabetic is that fruits also contain sugars that can spike your blood sugars so vegetables or supplements may be a safer option.
Should diabetics take Vitamin C supplements?
Diabetes causes oxidative stress because of fluctuating blood glucose levels.
This stress is what causes damage to blood vessels increasing the risk of heart disease and other complications.
Properly managing blood glucose levels in combination with taking 500 mg of vitamin C daily can reduce oxidative stress in type 2 diabetics. This lowers blood pressure and decreases the risk of blood vessel damage.
More research is needed for type 1 diabetics.
If you think taking vitamin C supplements may be of benefit to you have a discussion with your doctor. Always follow your doctor’s advice.
Sometimes vitamin C is taken for heart health however women need to be careful they don’t take too much vitamin C as it may do more harm than good.
Type 1 diabetes
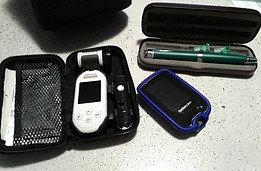
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disorder in which the body’s own immune system attacks and kills the insulin-producing Beta cells in the pancreas leaving the person unable to produce insulin.
Insulin is required in order for our cells to be able to absorb the glucose(sugar) from our food to be used for energy.
Without insulin, our cells do not get the energy they need.
Type 1 diabetics must take insulin either by injection or pump daily.
Our 6-year-old grandson lives with type 1 diabetes and endures countless finger pricks and a minimum of 4 injections each day of his young life.
There is no cure for type 1 diabetes and proper management is essential in order to minimize the risk of complications like heart disease, stroke, blindness, or even amputation.
Symptoms of type 1 diabetes may include:
Symptoms of type 1 diabetes usually come on suddenly over the course of just a few weeks and may include:
- frequent urination
- excessive thirst
- unexplained weight change (gain or loss)
- extreme fatigue
- blurred vision
- cuts or sores that either don’t heal or take longer than usual to heal
- recurring infections
- tingling or numbness in hands or feet
- trouble getting or maintaining an erection(men)
- diabetic ketoacidosis(DKA)
Diabetes management includes
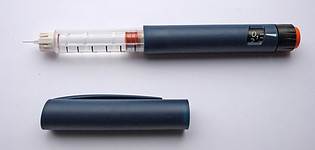
Managing type 1 diabetes is very individualistic. Your diabetes care team will determine the best treatment plan for you. Most diabetes management plans include:
- frequent testing of blood glucose(sugar) levels
- administering insulin when required
- eating fast-acting sugar snacks when blood sugars drop too low
- eating a healthy, well-balanced diet
- getting regular daily exercise
- ensuring you get adequate sleep
Always follow the advice given by your diabetes care team.
How does vitamin C affect type 1 diabetes?
While very similar, type 1 and type 2 diabetes are very different but they can both benefit from increased vitamin C.
Often, vitamin C levels are found to be low in type 1 diabetics.
Increasing the amount of vitamin C in the bloodstream will also help lower the amount of sorbitol.
What is sorbitol?
Sorbitol is a type of sugar that is harmful when it accumulates.
The presence of sorbitol increases the risk of retinopathy, neuropathy, and kidney damage.
Studies have also shown that combining insulin with vitamin C stops blood vessel damage in type 1 diabetics.
Type 2 diabetics may find that increasing their vitamin C helps improve their glucose tolerance.
Final thoughts
So there we have it.
Throughout this article, we have learned just how does vitamin C affects type 1 diabetes.
While research is ongoing increasing your vitamin C may reduce oxidative stress from fluctuating blood glucose levels that cause blood vessel damage.
Vitamin C may help type 2 diabetics improve their glucose tolerance.
There are a variety of fruits and vegetables that contain various amounts of vitamin C.
Vitamin C can also be taken in supplement form.
Anytime you are considering dietary changes or adding supplements be sure to consult with your diabetes management team.
Always follow your doctors’ advice.
I realize that everyone can benefit from vitamin C but in this article, I was focused on how it affects diabetics.
I am not in any way a medical practitioner. Please do not rely on the information on our website as an alternative to medical advice from your doctor or another healthcare provider. We only share our experiences. We are affiliates, this means that if you purchase something from a link or ad on this site we may receive a small commission. This in no way affects the price you pay.
Do you or someone you know take Vitamin C?
How do you take your vitamin C?
Supplements?
or
eating a variety of vitamin C-rich fruits and vegetables?
Share your experiences in the comment section below.

